Podcast: Play in new window | Download
Episode 3: PFAS comes out of the body during Ionic Foot Bath.
Download the Ambassador Slides HANDOUT to share.
Introduction
Polyfluoryl-alkyl Substances (PFAS) represent 15,000 different variations of long chains of fluoride, a known neurotoxin, that bioaccumulate in plants and animals.1 In humans, they have been associated with kidney cancer, increased cholesterol, and thyroid problems to name a few.2 PFAS is commonly referred to as “forever chemicals” due to the fact they stay in the body from 3-27 years, depending on the form.3 Ongoing bioaccumulation risks remain for those working in industries with frequent exposure, dump sites, contaminated water supplies, food packaging, painting, electroplating, carpet installation, carpet treatment, serving as a firefighter, working with ski wax, waterproofing material and construction materials.1, 4 Public awareness has not yet caught up to the existing science and there is a paucity of recommendations available for the informed consumer.
The available data for daily exposure for the general population to PFAS comes out of Canada and Norway.5 Daily consumption was 90% dietary with intake of 73 ng/day, on par with dust and air inhalation exposure. A follow-up study combined types of PFAS and estimated daily consumption as high as 250 ng per day. This study aims to validate ionic foot bath treatments remove PFAS from the human body, paving the way to correlate with improved health outcomes.
This study analyzes the removal of PFAS from a human subject by an inexpensive ionic foot bath machine.
Materials
- Hand-crafted copper foot basin from India
- Ionic Cleanse Detox machine from Better Health Company, round double coil array. Model BHC-CTRL-01, 24 W, 2A, 12V DC.
- One gallon per session of distilled water, steam distillation from Premium Waters, packaged 05/27/24 12:06, best by 05/27/2025.
- GreenPan anodized ceramic cooking pot
- Pink Himalayan salt, 1/4 cup per session
Methods
An initial serum PFAS level was obtained using the PFASure test from Any Lab Test Now.
One 30-minute foot bath session was conducted with the Ionic Cleanse Detox Machine using distilled water with 1/4 cup of pink Himalayan salt.
Water sample testing was conducted on both the clean and dirty foot bath water using SimpleLab.
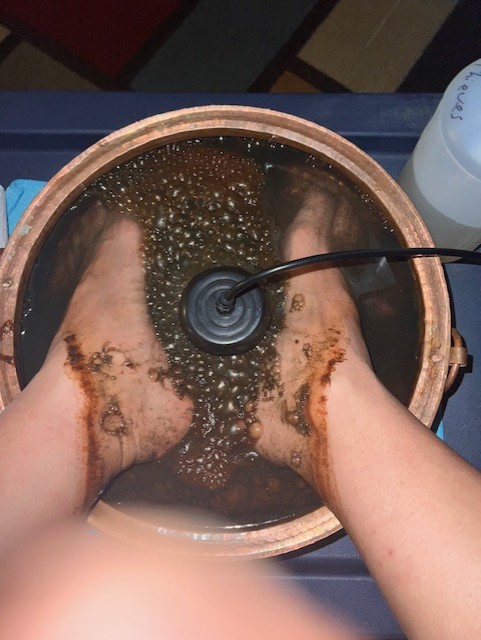
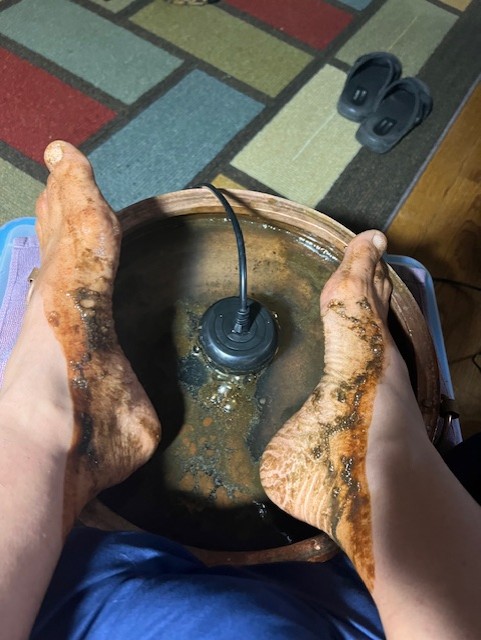

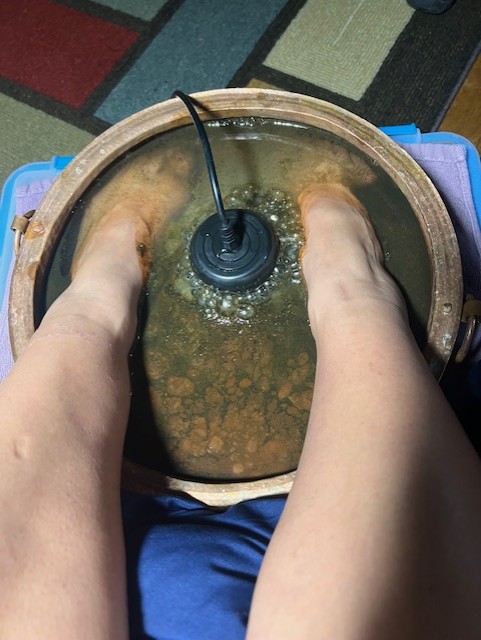

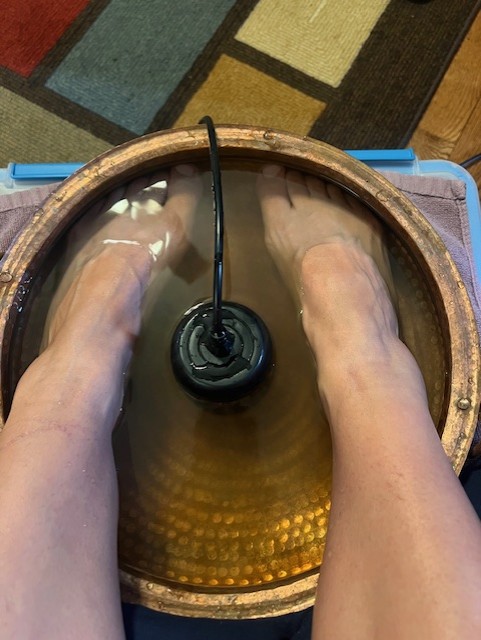

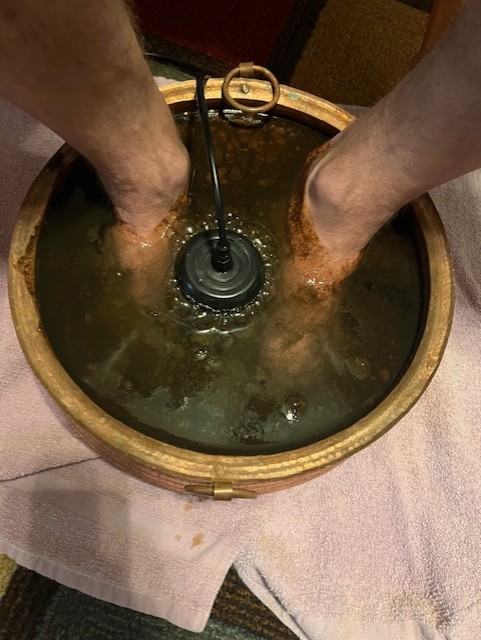
Results
The initial serum PFAS result was 7 ng/mL, which falls in the Medium Risk Category (<2 preferred, 2-20 elevated risk health risks, >20 high risk of bad health outcomes).
The clean sample of distilled water used in the initial foot bath came back from the lab totally free of PFAS.
The dirty water from my very first foot bath was also sent off for 3rd party, independent testing. The PFAS results was 49.7 PPT (parts per trillion), which is over 12 times the new EPA drinking water standard (<4 PPT). The lab results is below:
| Initial Values | Unit Conversions |
| 0.0000497 PPM | mg/L |
| 0.0497 PPB | microgram/L |
| 49.7 PPT | ng/L |
| 49,700 PPQ | pg/L |
Discussion
This study will need to be duplicated if it turns out that PFAS comes out readily during electrolysis.
Recommendations
The PFAS Detox: Mindshift Care Protocol
My Recommendations are a work-in-progress as I post my progress on the Gluten-Free Psychiatry Podcast.
Updated 2/11/2025
STAGE 1:
Limit exposure. Filter water all the time.
Ionic foot baths or sauna.
Educate yourself.
Creative Visualization and Meditation of being fully detoxed.
STAGE 2:
Ketosis to kill fat cells storing toxins.
Next Steps
I’ll post more data here as the protocol goes along the next few months, including final serum PFAS testing and clean water data. From these data, we’ll be able to estimate the following:
- Quantitative amount of PFAS excreted through the feet during electrolysis.
- Rate of electrolysis excretion of PFAS to estimate the number of treatments needed.
References
1. National Academies of Sciences E, Medicine, Health, et al. The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National Institutes of Health. Guidance on PFAS Exposure, Testing, and Clinical Follow-Up. National Academies Press (US)
Copyright 2022 by the National Academy of Sciences. All rights reserved.; 2022.
2. Joglekar R, Liddie J, Olson ED, Faber S, Schnettler J. The Environmental Justice Implications of PFAS. Env’t L Rep. 2024;54:10911.
3. Williams DM. Early Potential Biomarkers of Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Bioaccumulation. Chart reviews were conducted for patients attending a psychiatric urgent care in Springfield, MO in July 2024. Inclusion criteria was having had a full panel of laboratory studies within the previous 18 months. Labs had to include a Vitamin D level, full lipid panel and full thyroid panel with at least TSH, T4 (conjucated/unconjucated), and T3 . Exclusion criteria were patients missing laboratory studies for either Vitamin D, lipid panel or thyroid panel. Age, gender, number of medical diagnoses, vitamin D supplement usage, TSH, T4 (or free T4), T3, total cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL, calculated VLDL, calculated HDL, and statin use were studied. Gluten-Free Psychiatry Podcast blog. 10/04/2024, 2024. https://mindshiftcare.com/early-potential-biomarkers-of-polyfluoroalkyl-substances-pfas-bioaccumulation/
4. Snedeker SM. Toxicants in Food Packaging and Household Plastics: Exposure and Health Risks to Consumers. Molecular and Integrative Toxicology. Springer; 2014.
5. Tittlemier SA, Pepper K, Seymour C, et al. Dietary Exposure of Canadians to Perfluorinated Carboxylates and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate via Consumption of Meat, Fish, Fast Foods, and Food Items Prepared in Their Packaging. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2007/04/01 2007;55(8):3203-3210. doi:10.1021/jf0634045

